|
1. Suggestions for Prayer, Study, and Action
|
"Merciful God, we confess that too often we find ourselves in the service of money rather than God. Out of a desire for cheap energy we have destroyed what you have created. We have put our own needs ahead of those of our neighbors and children by using the creation you have blessed us with in ways that steal both its beauty and usefulness from future generations. We have sinned in what we have done, and in what we have left undone. It is easy for us to go through the day and not realize how many people are affected by our daily energy use. Forgive us our sins, and guide us as we struggle to live in a way that is pleasing to you. Amen."
Source: NCC Ecojustice.
|

|
|
|
THE EARTH BELONGS TO EVERYONE
This book by Earth Rights Institute Co-Director Alanna Hartzok presents a large and hopeful world view with profound possibilities for transformational action for economic justice and environmental restoration. The book is a collection of 30 essays on themes such as:
- Democracy, Earth Rights and the Next Economy
- Restructuring Economic Relationships
- Land for People, Not for Profit
- Ecotaxes and Citizen Dividends
- Financing Local to Global Public Goods
- Women, Earth and Economic Power
- Economics of War and Peace
- Land Value Tax and Resource Rent
- Citizen Dividends and Oil Rent
- The Alaska Permanent Funf
|

|
|
2. News, Publications, Tools, and Conferences
|
NEWS
|
PUBLICATIONS
|
| |
| |
TOOLS & DATABASES
|
| |
|
CONFERENCES & JOURNALS
|
| |
|
|
3. Advances in Sustainable Development

Humanity Can and Must Do More with Less, UNEP Press Release, 12 May 2011
Download UNEP Report
Download UNEP CHARTS
4. Advances in Integral Human Development
|
Gender equality between aspirations and realities,
Ioan Voicu, Assumption University, Bangkok, Thailand. Online Opinion: Australia's e-journal of social and political debate, 29 June 2011.
Global Civics: Responsibilities and Rights in an Interdependent World, Hakan Altinay, ed., Brookings Institution, 2011.
Conscious Leadership for Sustainability, Barret Brown, Fielding Graduate University, April 2011.
Leadership for Sustainability, Judi Marshall, Gill Coleman, and Peter Reason, Greenleaf Publishing, 2011.
Human Development Index and the Ecological Footprint, Global Footprint Network, 10 February 2011.
Population 7 Billion, Robert Kunzig, National Geographic, January 2011.
The Real Wealth of Nations: Pathways to Human Development, Human Development Report (HDR), United Nations, 4 November 2010.
International Human Development Indicators, Human Development Index (HDI), United Nations, 4 November 2010.
The HDI includes demograhic, health, education, income, inequality, poverty, gender, sustainability, and human security factors. Several analysis options are available:
To plot combinations of HDI factors and ranks by country in linear or log scales, click here
To view HDI trends for any combination of countries and factors, click here
To customize the index by selecting any combination of factors, click here
To partition the HDI data by more specific subsets of the above 9 factors, click here
To build tables for any combination of countries, indicators, and years, click here
The resulting subsets of data can be downloaded as spreadsheets for further analysis. For example:
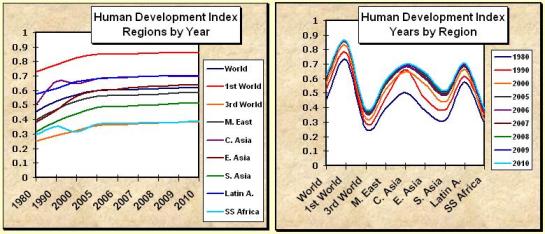
1980-2010 Human Development Index Trends by Year and by Regions
Based on the Human Development Index 2010 Database
It is worrisome that human development - as measured by the HDI - seems to be flattening in recent years for all regions. When only the end-of-decade (1980, 1990, 2000, 2010) data points are plotted, the flattening is not so apparent but it is still evident that human development has not kept pace with the explosive growth in financial wealth after 1990, which persists even after the 2008 financial debacle. In either case, when the year by year differences are plotted by region, the geographic distribution of human development exhibits wide and persistent inequalities between regions. Neither the flattening nor the inequalities of human development trends bode well for the future of human civilization.
|
5. Advances in Integrated Sustainable Development

Ryan Katofsky, Matthew Stanberry & Lisa Frantzis, Navigant Consulting, Inc.
Workshop on "Renewable Energy: From Analysis to Action"
IEA Renewable Energy Technology Deployment Implementing Agreement
OECD Conference Center - Paris, 15-16 March 2011
To download the report, click here
|
Making Rio 2012 work: Setting the stage for global economic, social and ecological renewal, Alex Evans and David Steven, New York University, June 2011.
The Building Technology Showcase, Fraunhofer Center for Sustainable Energy Systems, May 2011.
Energy Report & Scenarios 2000-2050, World Wide Fund for Nature, February 2011.
Green Economy Report, United Nations Environmental Program, February 2011.
|
6. Sustainability Games, Databases, and Knowledgebases
7. Visualizations of the Sustainable Development Process
|
Sustainable Land Development Inititiative, TriplePundit, 2 December 2010.

Source: TriplePundit
|
This is a hierarchical model that visualizes sustainable development in terms of three interacting dimensions, each with three interaction sub-dimensions:
Profit (economics)
Create Value
Eliminate Waste
Recognize Interdependence
Planet (the human habitat)
Natural Resources
Energy Flows
Humans & Nature
People (society)
Share Knowledge
Accept Responsibility
Quality of Life
|
Fifteen Global Challenges for Humanity, Millennium Project, 2010.

Source: Millennium Project
|
The lines show all the interactions between 15 challenges facing humanity. It provides a better visualization of the complexity of the process.
Assuming that the 15 challenges can be analyzed in groups of 5, the number of group combinations to be analyzed is 15!/10!5!, or 3003. If the order in which they are considered matters, then the number of challenge permutations to be analyzed is 15!, or 1307674368000.
Computers can crunch numbers, but resolving these 15 challenges together requires more than number crunching.
|
The Perfect Recipe, Concita Ladelfa, EuroEcoTeens.Net, Energy and Environment Comenius Project, 23 November 2010.

Source: Comenius Project
|
This is the best visualization. It shows that, in the ultimate analysis, the transition from consumerism to sustainability must happen in human minds and hearts before it can happen at any level - local, national, or global.
This model suggests the additional (and critical) insight that the transition is contingent on gender equality and cross-gender solidarity. Sustainable development will require the collaboration of all men and women of good will.
The transition from homo economicus to homo ecologicus requires gender equality, because the ecological mindset cannot take root and grow as long as humans are engaged in any form of domination; and patriarchy is the most pervasive structure of domination.
|
|
8. Sustainable Development Modeling and Simulation
|

Energy infrastructures as socio-technical systems
Simulating Energy Transitions, Emile Chappin, Delft University, 16 June 2011, Figure 1.2, page 3.

Electricity and CO2 prices and CO2 emission levels for three carbon policies
Simulating Energy Transitions, Emile Chappin, Delft University, 16 June 2011, Figures 4.13a and 4.13b, page 110.
|
9. Sustainable Development and the International Community
|
|